How Osteopathy can Treat Sports Injuries
Are Sports Injuries Holding You Back?
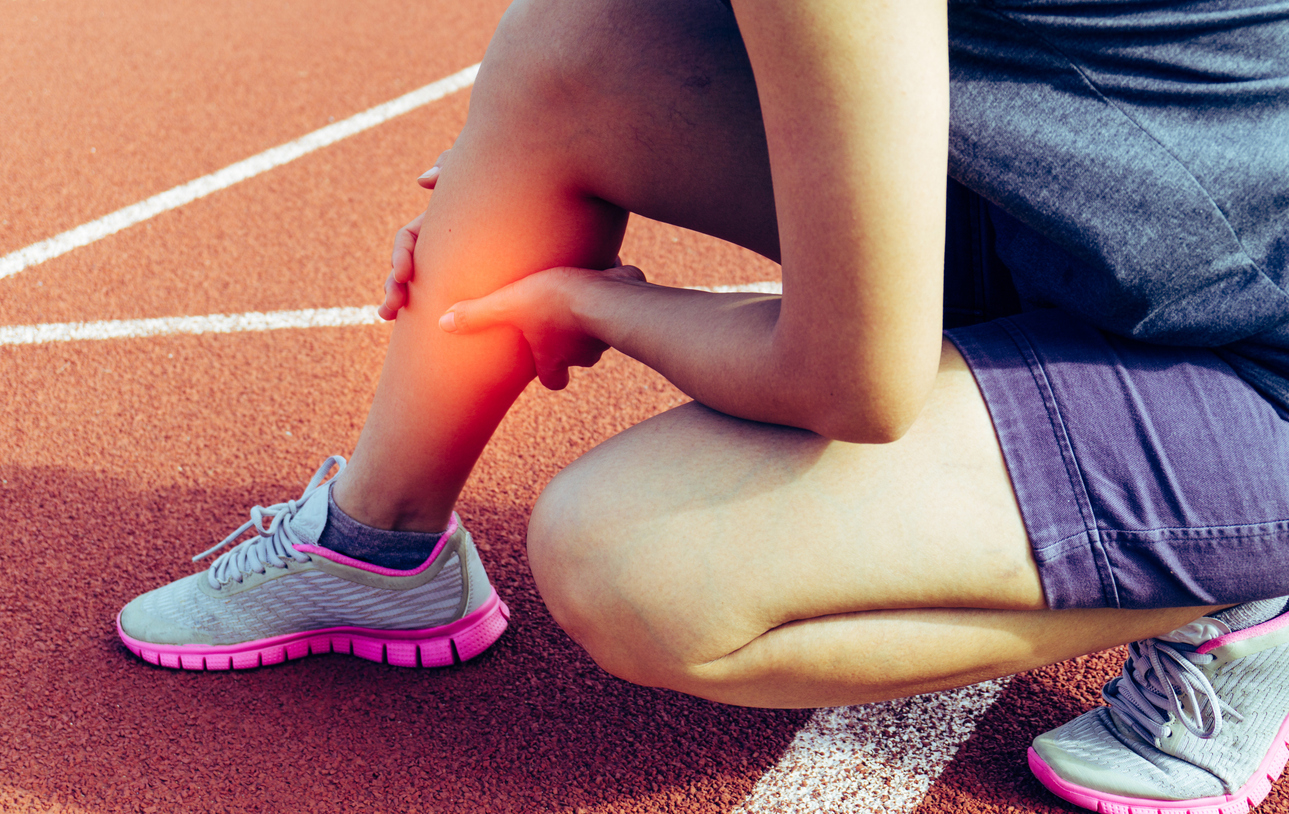

Understanding Sports Injuries
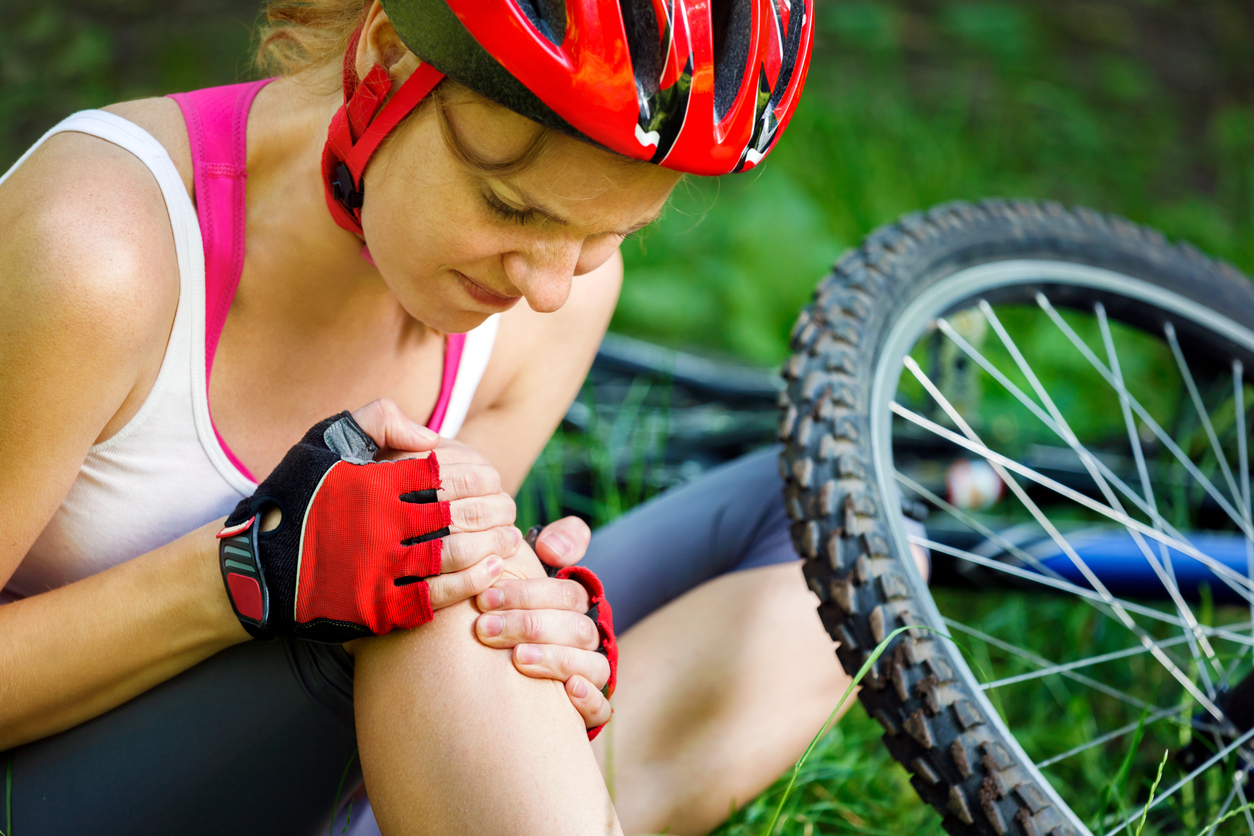

Sports injuries can range from acute issues like sprains, strains and fractures, to chronic conditions, such as tendonitis or joint pain caused by repetitive stress. These injuries often result from factors like overuse, poor technique, lack of proper warm-up or underlying imbalances in the body. Traditional treatments may focus solely on the injured area, but osteopathy takes a broader approach, addressing the body as a whole and using non-invasive methods free of medication to target the root causes of your pain and promote overall healing.
What Is Osteopathy?
Osteopathy is a type of manual therapy that focuses on the musculoskeletal system, which includes muscles, bones, joints and connective tissues. Osteopaths use hands-on techniques to assess and treat the body, aiming to restore natural balance, improve mobility and enhance the body’s own natural healing processes. This approach is particularly beneficial for sports injuries, as it not only treats the symptoms but can also help to prevent future issues.
How Osteopathy Helps with Sports Injuries
Pain Relief and Reduced Inflammation
One of the primary benefits of osteopathy is its ability to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Techniques like soft tissue massage, joint mobilisation and myofascial release can help improve blood flow to the injured area, reducing swelling and promoting faster healing.
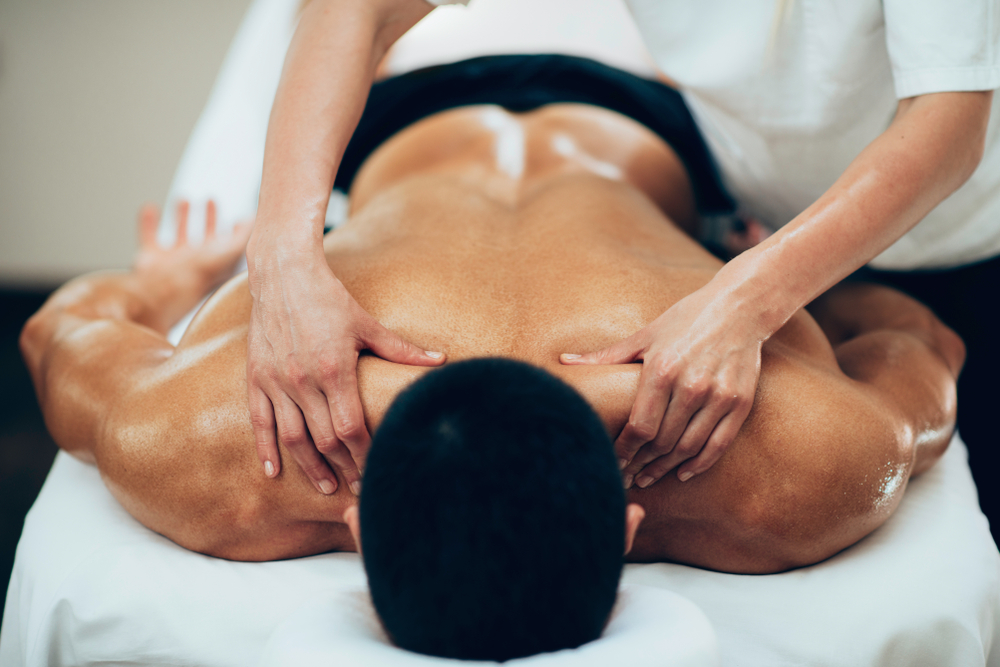
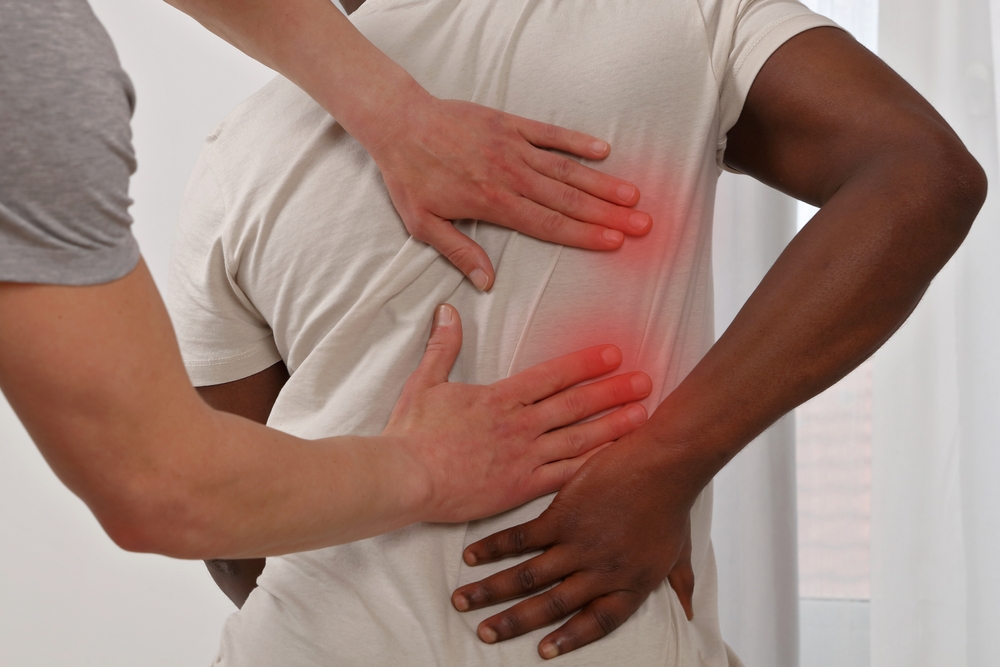


Improved Mobility and Flexibility
Sports injuries often lead to stiffness and restricted movement. Our osteopaths work to restore mobility by addressing tight muscles, stiff joints, and scar tissue. This is especially important for athletes who need a full range of motion to perform at their best.
Identifying Underlying Issues
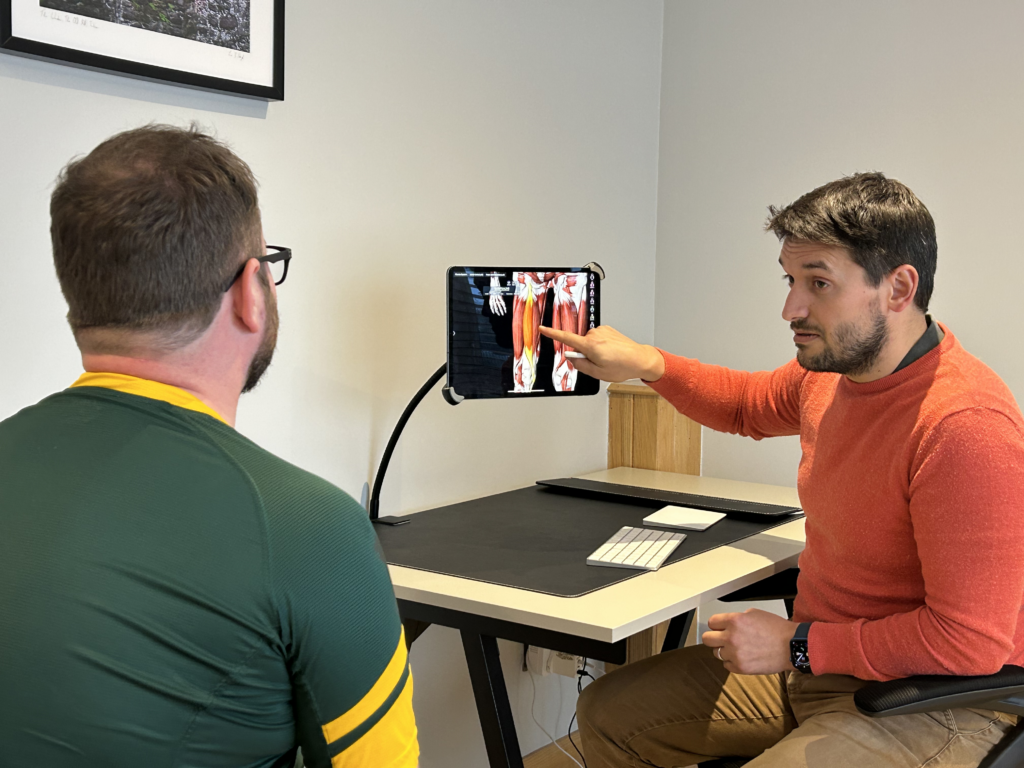
Many sports injuries are caused by imbalances or weaknesses in the body. For example, poor posture, uneven muscle strength or improper alignment can potentially increase the risk of injury. Osteopaths conduct a thorough assessment to identify these underlying issues and create a personalised treatment plan to address them.
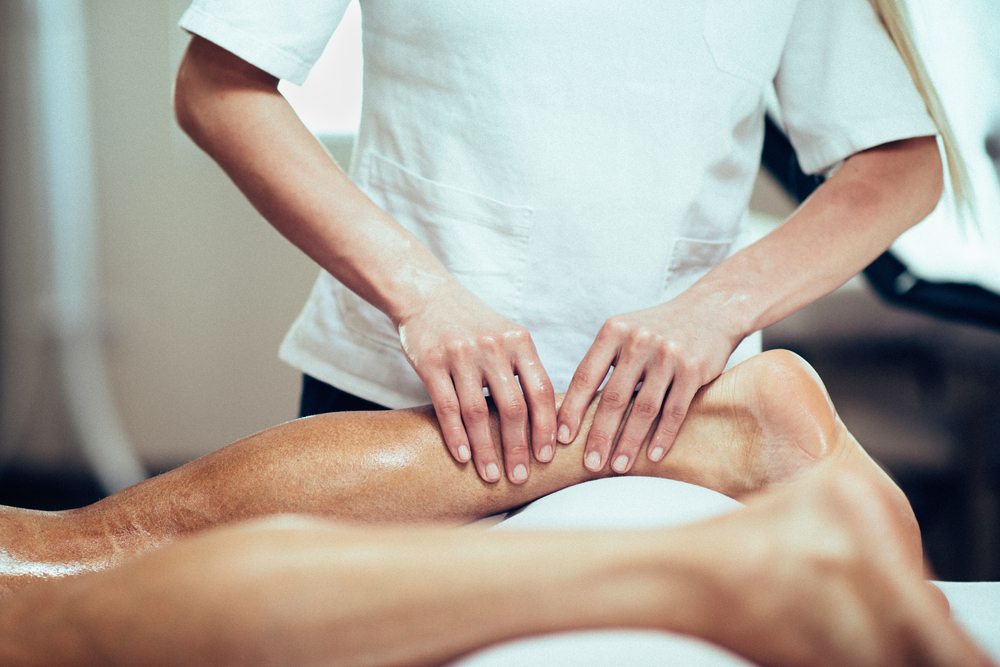


Prevention of Future Injuries
By correcting imbalances and improving biomechanics, osteopathy not only treats current injuries but also reduces the likelihood of future ones. As part of a treatment plan, our clinicians will often provide advice on posture, technique, and stretching exercises tailored to your sport or activity.
Holistic Recovery Support
Osteopathy recognises that recovery involves more than just treating the injury. It takes into account factors like stress, sleep, and overall health, which can impact the healing process. Osteopaths may recommend lifestyle adjustments to support a quicker and more complete recovery.
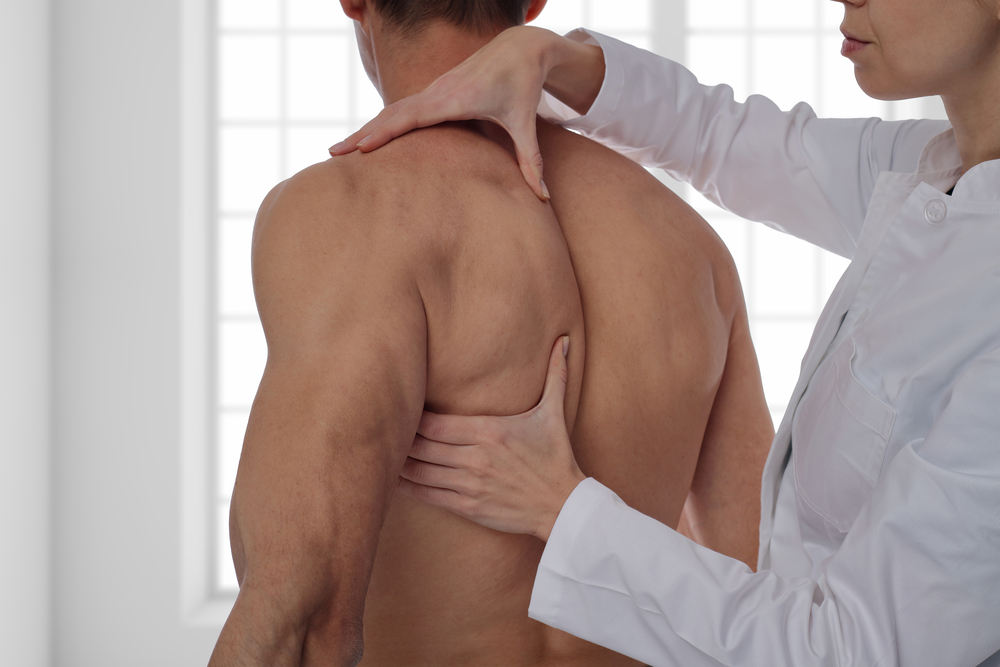
Common Sports Injuries Treated with Osteopathy
Osteopathy can help manage a variety of chronic pain conditions.
Sprains and Strains
Ligament and muscle injuries caused by overstretching or tearing.
Tendonitis
Inflammation of tendons due to repetitive motion.
Shin Splints
Pain along the shinbone caused by overuse.
Back Pain
Common in athletes due to improper lifting techniques or sudden movements.
Runner’s Knee
Pain around the kneecap often caused by overuse.
Benefits of Osteopathy for Chronic Pain
Non-Invasive and Drug-Free
Osteopathy offers a safe alternative for those seeking pain relief without relying on medications or invasive procedures.
Personalised Care
Treatment plans are tailored to each individual’s needs, ensuring the best possible outcomes.
Long-Term Results
By addressing the root causes of pain, osteopathy provides lasting relief rather than just masking symptoms.
Why Choose Osteopathy for Sports Injuries?
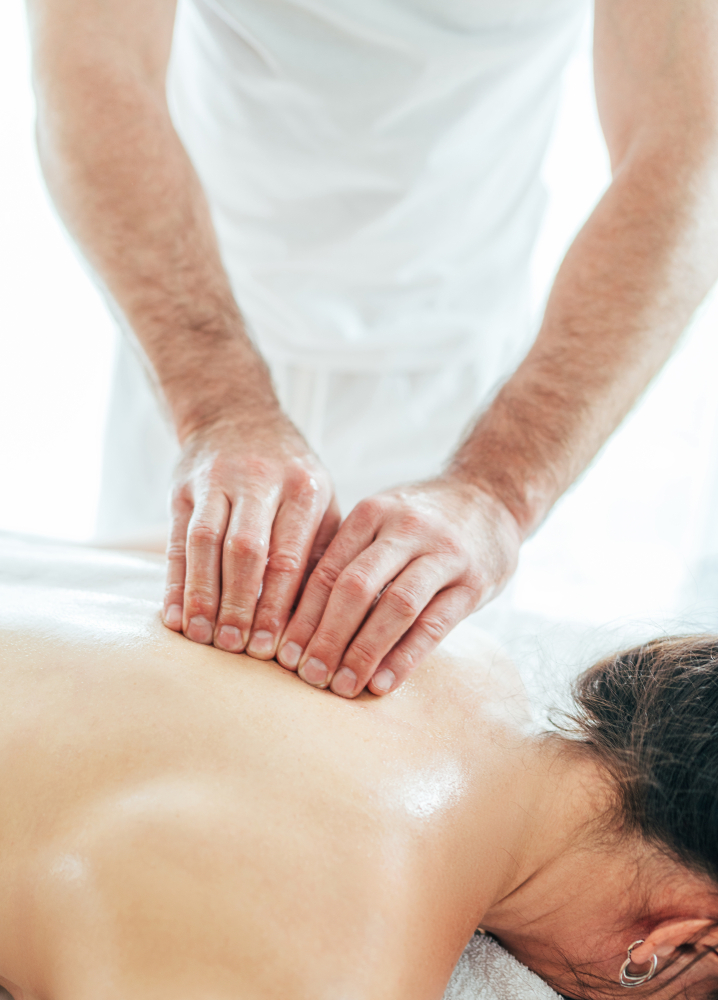
Unlike treatments that focus solely on the injured area, osteopathy takes a whole-body approach. This ensures that all contributing factors are addressed, leading to more effective and lasting results. Additionally, osteopathy is non-invasive and drug-free, making it a safe option for athletes and fitness enthusiasts of all levels.
Sports injuries don’t have to sideline you for long. With the help of osteopathy, you can recover faster, improve your performance and reduce the risk of future injuries. By addressing the root causes of pain and dysfunction, osteopathy offers a comprehensive solution that supports both immediate recovery and long-term health.
Book an appointment
If you’re struggling with a sports injury or want to optimise your physical performance, consider Just One Body. Contact us to arrange an appointment to see how our experienced osteopaths can help you, or alternatively use the quick and easy online booking system. Click the link here to read more of our blog posts.

